Hardware-Software AI based Co-design for Quantum Systems – Developing a scalable quantum ecosystem by combining quantum computing with a unique topological approach, and advancing silicon-based quantum chips by leveraging deep expertise in semiconductor technologies
A smart sensor platform that monitor appliances – level energy use in real-time AI running on a low power FPGA chip
Our product serves both green building operators aiming to reduce carbon emission and healthcare providers supporting aging in place strategies

FPGIA
AI Technology and HW Development
Our solution on using AI in the development and product lifecycle for FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays) has the potential to bring several significant advantages, streamlining processes and improving performance across different stages, from design to deployment. Here’s how AI can contribute to FPGA development and products:
1. AI-Assisted FPGA Design Automation
- Enhanced Design Space Exploration: AI can automate design space exploration by using machine learning algorithms to quickly identify the best configurations for power, performance, and area (PPA). This optimization can significantly speed up the process of selecting the most efficient FPGA architectures based on the application needs.
- Auto-Design Tools: AI-based tools can assist designers in creating complex hardware systems for FPGAs. Tools like High-Level Synthesis (HLS) that use AI can help convert high-level code (C, C++) into FPGA-optimized designs, reducing the manual effort required for low-level design tasks such as logic synthesis, placement, and routing.
- Intelligent IP Block Generation: AI can be used to design new IP blocks automatically or modify existing ones to suit specific tasks. This can drastically reduce time-to-market by generating custom hardware solutions based on real-time performance requirements.
2. AI-Powered Verification and Testing
- Automated Testbench Generation: AI can automatically generate testbenches to verify FPGA designs. It can learn from past verification efforts and generate a comprehensive set of test vectors that focus on edge cases and potential design bugs.
- Predictive Error Detection: Machine learning models can be trained to identify patterns in previous verification cycles, predicting the likelihood of errors or areas in the design that may need additional testing. This predictive verification reduces debug time and improves product reliability.
- Dynamic Performance Testing: AI can be employed to create self-adjusting testing environments for FPGA-based systems, where test conditions can be modified in real-time based on the performance of the device under test, improving efficiency in testing complex systems.
3. AI for FPGA Resource Optimization
- Power and Performance Tuning: AI algorithms can optimize power consumption dynamically by adjusting FPGA resources and clock frequencies based on the workload. Machine learning can fine-tune the balance between power and performance at runtime, allowing for adaptive computing based on real-time conditions.
- AI-Driven Floorplanning and Routing: AI can assist in the FPGA placement and routing phase, where it optimizes the layout of components to minimize resource usage, latency, and interconnect congestion, resulting in faster and more efficient FPGA designs.
- Resource Utilization Prediction: AI models can predict how much FPGA fabric and resources (like LUTs, DSPs, and BRAMs) will be required for certain designs, ensuring that hardware resources are effectively utilized without over-provisioning.
4. AI-Enhanced FPGA-Based Product Development
- Real-Time Data Processing: FPGAs are known for their parallel processing capabilities, and integrating AI with FPGA systems can boost their ability to handle large-scale real-time data processing. This is especially useful in AI/ML applications such as real-time video processing, signal processing, and autonomous systems.
- Edge AI and Inference Acceleration: AI algorithms like deep learning models can be deployed on FPGA-based systems for inference acceleration. AI frameworks can leverage the reconfigurability of FPGAs to provide hardware acceleration for tasks like computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), and object detection.
- FPGA-Based AI Models: AI tools can be used to generate efficient hardware implementations of AI models, such as neural networks, which can then be deployed on FPGAs for ultra-low-latency inferencing in applications like automotive systems, industrial automation, and smart cameras.
5. AI in FPGA Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- AI for Predictive Maintenance: AI can be integrated into FPGA-powered systems to monitor their performance in real-time and predict potential failures or degradation. This predictive maintenance approach extends the product lifecycle and ensures the reliability of FPGA-based products in critical applications.
- Intelligent System Updates: AI can enable real-time learning in FPGA-based systems that allows for intelligent, autonomous updates. These systems can adapt to changing requirements or conditions in the field without manual intervention, improving long-term performance and reliability.
- Product Customization and Adaptation: AI-driven insights can help create FPGA solutions tailored to specific customer needs by analyzing data and trends. For instance, it can help generate specific AI models to run on FPGAs that suit a particular application, making product customization faster and more efficient.
6. AI-Driven Performance Profiling and Optimization
- Hardware-Software Co-Design: AI can assist in optimizing hardware-software co-design by profiling application performance on FPGA-based systems. It can help balance the computational load between hardware and software, optimizing overall system performance for a particular application.
- Performance Monitoring and Optimization: AI models can monitor FPGA systems’ performance during real-world operation, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies. By learning from this data, AI can help optimize configurations for future designs or dynamically adjust FPGA settings to improve efficiency during operation.
7. AI for Security in FPGA Development
- Enhanced Security Verification: AI can be used to automatically detect potential security vulnerabilities in FPGA designs, such as side-channel attacks, hardware trojans, or backdoors. Machine learning models can identify patterns in RTL code or hardware implementations that may be prone to exploitation.
- AI-Based Intrusion Detection: AI can be deployed in FPGA-based systems to monitor real-time data traffic and detect anomalous behaviors or intrusions, improving the security of FPGA systems deployed in critical applications such as automotive, aerospace, or defense.
Integrating AI into FPGA development and product lifecycles provides the opportunity to accelerate design processes, enhance verification, and optimize system performance. AI also helps in creating more intelligent and adaptive FPGA-based solutions, which are vital for emerging applications in edge computing, real-time processing, and autonomous systems. Ultimately, AI in FPGA development ensures faster time-to-market, improved performance, and increased flexibility, making it an essential tool for next-generation hardware design.
QCore
Designing the QCore Quantum Chip
Our solution involves creating a silicon-based quantum processing unit that integrates quantum bits (qubits) with control and readout circuitry. The goal is to achieve scalable, stable, and efficient quantum operations by leveraging semiconductor manufacturing techniques, enabling compatibility with existing fabrication infrastructure and supporting future quantum computing applications
1. Define Purpose
Determine the application of QCore: gate-based quantum computing or quantum annealing for optimization tasks.
2. Select QCore Technology
Choose the underlying quantum technology for QCore:
- Superconducting circuits
- Trapped ions
- Photonic systems
- Silicon spin qubits
3. Cryogenic Environment
Design QCore to operate at millikelvin temperatures using a dilution refrigerator or other cryogenic platforms.
4. Control & Readout Electronics
Integrate low-noise microwave/RF control lines for QCore
- Multiplexed readout circuits
- Scalable I/O interfaces
- Interface with ASIC/ FPGA controllers
5. Fabrication Process
Use CMOS-compatible or custom nanofabrication for QCore elements:
- Patterning Josephson junctions
- Precision ion trap electrodes
- On-chip photonic routing (if applicable)
- Use CMOS-compatible or specialized quantum fabrication.
- Pattern Josephson junctions or ion traps with precision lithography
6. Characterization & Calibration
Test and calibrate QCore’s performance:
- Coherence times (T₁, T₂)
- Gate fidelity
- Crosstalk and readout errors
- Measure T1/T2, fidelity, and gate errors.
- Calibrate using randomized benchmarking.
7. Quantum Error Correction Integration
Implement quantum error correction on QCore using surface codes or similar schemes to build fault-tolerant logical qubits.

FPGA HOST PC
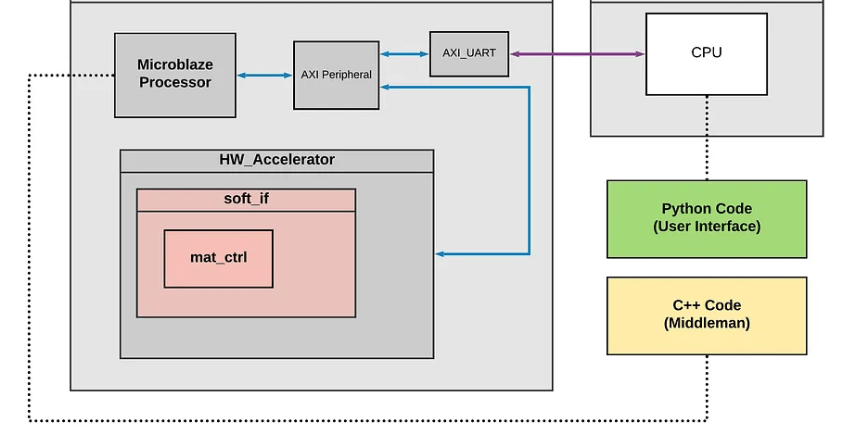
Quantum computing using FPGA/SoC design
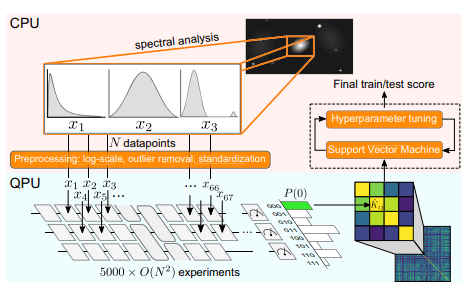
ML Data Analysis on Quantum Processor
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from theoretical research to practical applications, revolutionizing industries such as healthcare, automotive, finance, and consumer electronics. At the heart of this transformation lies the development of specialized hardware designed to accelerate AI workloads: AI chips. These chips are engineered to handle the massive computational demands of AI algorithms, particularly those involving machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL).